Capital costs for construction projects
Capital costs are costs associated with one-off expenditure on the acquisition, construction or enhancement of significant fixed assets including land, buildings and equipment that will be of use or benefit for more than one financial year.
Whilst it is generally relatively straight forward to identify expenditure to acquire or construct fixed assets, distinguishing between enhancements and 'revenue account' expenditure (sometimes called revenue expenditure or operational costs) such as repairs, maintenance, or replacement can be difficult.
Very broadly, capital enhancements should either:
- Significantly lengthen the life of the asset.
- Significantly increase the value of the asset.
- Significantly increase usefulness of the asset.
It is important to distinguish between capital and revenue account costs as there are significant accounting and taxation issues which stem directly from how a particular item of expenditure is treated. On a personal level, it can affect whether a particular transaction is subject to capital gains tax as opposed to income tax. In a commercial environment similar issues arise, as well as the possible entitlement to capital allowances, and how such treatment affects profitability.
The capital cost of developments can include:
- Land or property acquisition.
- Commissions.
- Statutory fees.
- Consultant fees directly associated with the development.
- Materials, plant and equipment.
- Labour.
- Fixtures and fittings.
- Project insurance, inflation, taxation and financing.
- Internal costs directly associated with the development.
Operational costs incurred in day-to-day operations might include:
- Wages.
- Utilities.
- Maintenance and repairs.
- Rent.
- Sales.
- General and administrative expenses.
In a commercial setting, accounting practice permits certain items of expenditure, which may appear to be operational in nature, to be capitalised, and a company's profitability can be enhanced or degraded according to how some items of expenditure are treated.
In construction and property these are complex issues, with additional complexity arising where a project may involve a combination of new build and repair and refurbishment.
On a new development it is common practice to capitalise items, such as consultants fees, which, on the face of it, would appear to be short term in nature. This is permitted under accountancy rules as such fees are an integral part of the development budget and so they may be included in the total capital cost of a scheme. By treating such fees as an 'asset' and including their value on the balance sheet, a company is enhancing its profitability as these fees would otherwise have to be set against the income of the company in question.
Capital allowances are tax deductible amounts which relate to specific categories of expenditure, most typically plant and equipment, and fixtures and fittings. By definition not all capital expenditure qualifies for capital allowances for example, consultants fees or Stamp Duty Land Tax.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Accounting.
- Budget.
- Business administration.
- Business plan.
- Capex.
- Capital.
- Capital allowances.
- Commercial management.
- Construction loan.
- Construction organisations and strategy.
- Cost.
- Cost-benefit analysis in construction.
- Cost reporting.
- Cost vs price.
- Hard costs v soft costs.
- Cost plans.
- Life cycle assessment.
- Life Cycle Costing BG67 2016.
- Net Present Value.
- New Rules of Measurement.
- Opex.
- Outturn cost.
- Price.
- Stamp duty land tax.
- Sunk cost.
- Whole life costs.
Featured articles and news
Twas the site before Christmas...
A rhyme for the industry and a thankyou to our supporters.
Plumbing and heating systems in schools
New apprentice pay rates coming into effect in the new year
Addressing the impact of recent national minimum wage changes.
EBSSA support for the new industry competence structure
The Engineering and Building Services Skills Authority, in working group 2.
Notes from BSRIA Sustainable Futures briefing
From carbon down to the all important customer: Redefining Retrofit for Net Zero Living.
Principal Designer: A New Opportunity for Architects
ACA launches a Principal Designer Register for architects.
A new government plan for housing and nature recovery
Exploring a new housing and infrastructure nature recovery framework.
Leveraging technology to enhance prospects for students
A case study on the significance of the Autodesk Revit certification.
Fundamental Review of Building Regulations Guidance
Announced during commons debate on the Grenfell Inquiry Phase 2 report.
CIAT responds to the updated National Planning Policy Framework
With key changes in the revised NPPF outlined.
Councils and communities highlighted for delivery of common-sense housing in planning overhaul
As government follows up with mandatory housing targets.
CIOB photographic competition final images revealed
Art of Building produces stunning images for another year.
HSE prosecutes company for putting workers at risk
Roofing company fined and its director sentenced.
Strategic restructure to transform industry competence
EBSSA becomes part of a new industry competence structure.
Major overhaul of planning committees proposed by government
Planning decisions set to be fast-tracked to tackle the housing crisis.
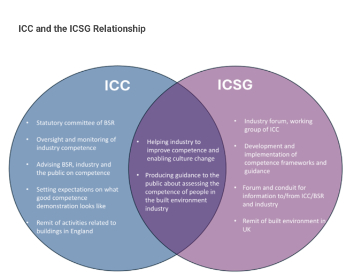
Industry Competence Steering Group restructure
ICSG transitions to the Industry Competence Committee (ICC) under the Building Safety Regulator (BSR).
Principal Contractor Competency Certification Scheme
CIOB PCCCS competence framework for Principal Contractors.
The CIAT Principal Designer register
Issues explained via a series of FAQs.























Comments